

 News
News Industry News
Industry NewsCommon dust sensors (also called PM2.5 sensors) on the market are divided into two categories: infrared dust sensors and laser dust sensors. Both infrared and laser dust sensors can be used to measure the concentration of particulate matter in the air. What is the difference between the two? You can compare them from the following aspects:
1.infrared dust sensors
The structure of the dust sensor based on the infrared principle is relatively simple. Its light source is an infrared LED light source. According to the principle of light scattering, the light emitted by the LED encounters dust to produce reflected light. The photosensitive detector detects the intensity of the reflected light and determines the dust concentration based on the size of the pulse signal. When no dust is detected, the photosensitive detector outputs a low pulse; conversely, when dust is detected, it outputs a high pulse.
2.laser dust sensors
Unlike dust sensors based on infrared principles, laser dust sensors are equipped with fans that can generate stable airflow. Once started, they can quickly obtain the PM2.5 concentration value in the current environment.
Because the laser dust sensor uses laser LED as the light source, its structure and circuit are more sophisticated than infrared sensors. When fine particles in the air are pushed into the area where the laser beam is located by the constant current fan, the laser will be scattered. We place a photodetector in an appropriate position so that it only receives scattered light, and then generates an electrical signal through the photoelectric effect of the photodetector. After circuit amplification processing, the concentration value of fine particles can be obtained.
Measurement accuracy
The infrared light source used by the infrared dust sensor has a long wavelength (about 700~900nm), and the measurement accuracy of particles with aerodynamic diameters less than 1um is insufficient. Because the particle signal scattered by infrared LED light is weak, it only has a relatively obvious response to large particles larger than 1um, and only uses heating resistors to drive the sampling airflow, the sampling number is small, and the measurement accuracy is about ±30%.
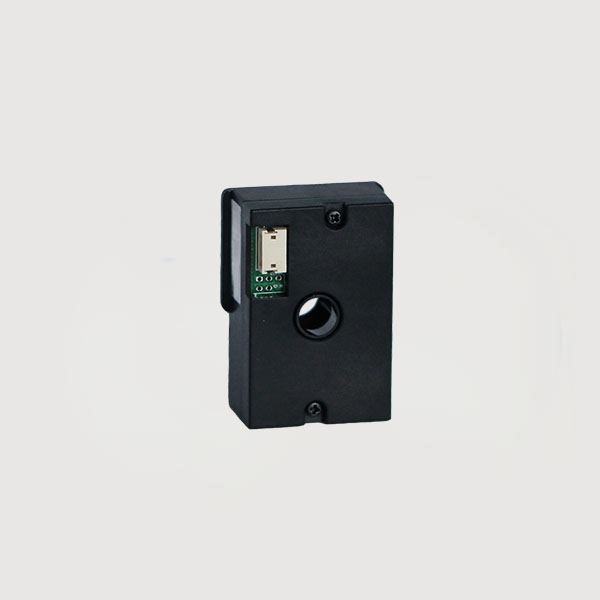

Laser sensors can detect dust particles as small as 0.3um. Because they have a higher performance MCU, use a constant speed fan to increase air intake, and collect higher density data, the overall measurement accuracy can reach ±10%. Therefore, laser dust sensors have obvious advantages in terms of sensitivity, accuracy, and consistency compared to infrared dust sensors in terms of measurement accuracy.

Application Scenario
Due to insufficient accuracy, infrared sensors are mainly used for industrial and mining dust, and the detection targets are large-particle and high-concentration dust, and cannot accurately measure the concentration of PM2.5.
Laser sensors are mainly used in the field of PM2.5 detection, quantifying the quality of PM2.5 with precision, and can be embedded in home (car-mounted, handheld) air detectors and air purifiers. In addition, laser sensors are also used in the fields of IoT data collection and environmental quality detection.
Tensensor laser dust sensors are widely used in dust detectors, purifiers, fresh air systems, smart homes, air conditioners and other fields.