

 News
News Industry News
Industry News In the fields of industrial safety, emergency response and even municipal construction, real-time monitoring of potentially hazardous gases is the lifeline for ensuring the safety of personnel and the normal operation of equipment. Among them, the "four-in-one gas detector" has become the standard equipment for on-site safety monitoring due to its comprehensive functions, portability and high efficiency.
Core Technology: How does the "four-in-one" "smart smell" work?
A four-in-one gas detector, as the name suggests, is an instrument that can simultaneously detect and display the concentrations of four common hazardous gases. These four gases typically include:
Combustible gases (LEL): Representative gases include methane and hydrogen.
Oxygen (O₂): Monitors oxygen-deficient or oxygen-rich environments.
Carbon monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless, and deadly gas.
Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S): A highly toxic gas with a rotten egg smell.
The core operating principle of this instrument is sensor technology. Different types of specialized sensors are integrated within the instrument for different gases.
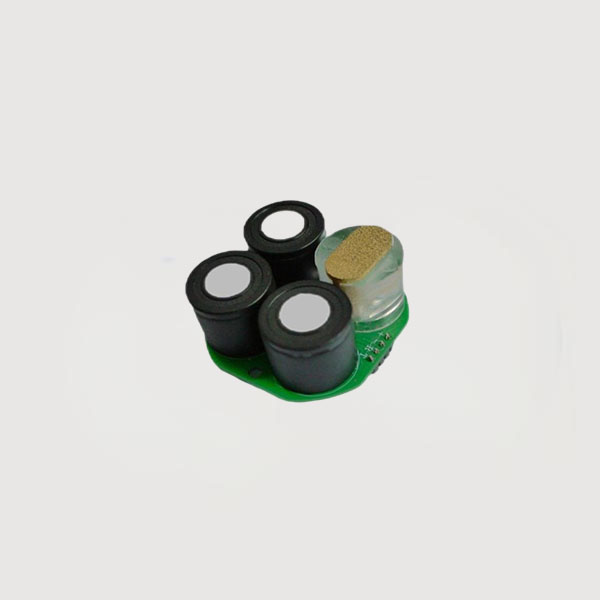

1. Combustible Gas (LEL) Detection: Catalytic Combustion Principle
The sensor contains a detection element and a compensation element, which together form a Wheatstone bridge circuit. When combustible gas enters the sensor, flameless catalytic combustion occurs on the surface of the detection element (a platinum wire coil coated with a catalyst). This causes its temperature to rise and its resistance to change, disrupting the bridge balance and generating an electrical signal proportional to the gas concentration. Compensation elements are used to compensate for interference caused by changes in ambient temperature and humidity.
2. Oxygen (O₂) Detection: Electrochemical Principle
Oxygen is reduced at the sensor's cathode, generating a diffusion current proportional to the oxygen concentration. By measuring this current, the oxygen volume fraction in the environment can be accurately calculated. Oxygen deficiency (<19.5%) can cause asphyxiation, while oxygen enrichment (>23.5%) significantly increases the risk of fire.
3. Carbon Monoxide (CO) and Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S) Detection: Electrochemical Principle
Both of these toxic gases are detected using electrochemical sensors. Gas diffuses through a diaphragm to the working electrode, where oxidation or reduction reactions occur under the action of a catalyst, generating a current signal proportional to the gas concentration. This sensor offers high sensitivity, fast response, and low power consumption, making it ideal for portable devices.
Market Application Scenario Analysis: Why Has It Become an "Industry Must-Have"?
The four-in-one gas detector's design accurately covers the core risks in most confined spaces and hazardous work environments, and its application scenarios are extremely broad.
1. Confined Space Entry - The "Gatekeeper" of Safe Access
This is the most classic and core application scenario for the four-in-one detector. According to OSHA, national standards, and other regulations, gas testing is mandatory before entering any confined space (such as storage tanks, reactors, underground pipelines, sewage wells, and fermentation tanks).
Testing Sequence:
Step 1: Oxygen Measurement: Confirms if there is a risk of asphyxiation or oxygen enrichment.
Step 2: Explosive Gas Detection: Confirms that the concentration of combustible gases is below 10% of the Lower Explosive Limit (LEL).
Step 3: Toxic Gas Detection: Confirms that the concentration of toxic gases such as CO and H₂S is within safe limits.
Market Drivers: Mandatory safety regulations in industries such as petrochemicals, municipal drainage, and warehousing and logistics are the primary factor driving the widespread adoption of this device.
2. Municipal Construction and Public Utilities - "Life Detectors" in Underground Spaces
Maintenance and inspection of urban underground pipeline networks (electricity, telecommunications, gas, and water supply) face complex and unpredictable gas environments.
Sewage wells/septic tanks: These are prone to producing high concentrations of H₂S and methane (a flammable gas), which deplete oxygen.
Gas pipeline inspection: Potentially leaked natural gas (primarily methane, a flammable gas) accumulates in confined spaces, posing a high risk.
Underground tunnels/pipelines: Poor ventilation can lead to oxygen deficiency or the accumulation of CO generated by internal combustion engines.
3. Emergency Rescue and Firefighting - Firefighters' "Second Pair of Eyes"
At fire scenes, chemical leaks, or after natural disasters, the gas composition of the environment changes rapidly.
Post-fire: Buildings may be filled with high concentrations of CO from incomplete combustion, and there is also the risk of oxygen deficiency in confined spaces due to collapse.
Chemical accidents: Quickly determine the presence of flammable or toxic gases at the scene, providing critical evidence for developing rescue plans and demarcating hazardous areas.
4: Petrochemical and Metallurgical Manufacturing - "Mobile Sentinels" on the Production Line
These industries themselves are sources of hazardous gas generation and use.
Equipment Maintenance and Hot Work: Before maintenance, inspect the interior and surrounding areas of the equipment to ensure hot work (welding, cutting) safety.
Daily Inspections: Workers wearing four-in-one detectors conduct patrol inspections of potential leak points, such as production equipment areas, pump rooms, and compressor stations, ensuring seamless safety monitoring coverage.
The four-in-one gas detector is more than just a simple combination of instruments; it's an integrated safety solution designed based on a deep understanding of industrial risks. It incorporates the working principles of multiple sensing technologies to ensure accurate and reliable detection. Its comprehensive coverage of core hazardous gases makes it an indispensable "electronic talisman" for protecting workers' lives and health in a wide range of scenarios, from routine inspections to emergency rescue operations. In today's world of growing safety awareness, correctly understanding and applying the four-in-one gas detector is crucial for companies to fulfill their primary safety responsibilities and achieve sustainable development.