

 News
News Industry News
Industry News With the rapid advancement of industrialization and urbanization, air quality has become a global focus. Among the many air pollutants, fine particulate matter (PM2.5) is considered an "invisible killer" due to its severe threat to human health. Accurate monitoring is the first step to effective governance, and dust sensors, as "frontline sentinels" that detect particulate matter concentrations in the air, are becoming an indispensable core component in intelligent environmental monitoring systems.
Dust Sensors: Principles and Core Technologies
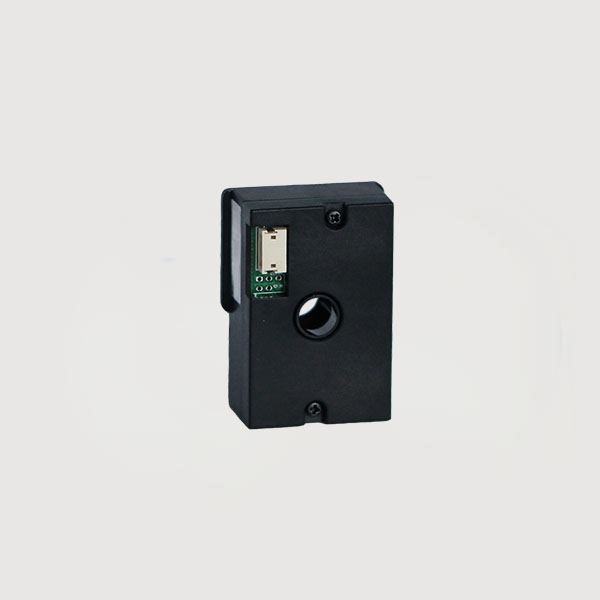
Dust sensors are devices specifically designed to detect the mass concentration of suspended particulate matter (such as PM2.5, PM10, dust, smoke, pollen, etc.) in the air. Currently, mainstream technologies are based on optical principles and can be categorized into light scattering and laser scattering.
The typical workflow is as follows: A fan or pump within the sensor forces a steady flow of measured air into the detection chamber. A light source (infrared LED or laser diode) within the chamber emits a steady beam of light. When particles in the air pass through the beam, they scatter, generating weak scattered light. A high-precision photodetector captures this scattered light and converts it into an electrical signal. A built-in microprocessor analyzes the signal using complex algorithms (such as Mie Theory) to ultimately calculate the particle mass concentration per unit volume (μg/m³).
Core Technology Comparison: Infrared vs. Laser
As you mentioned, dust sensors are primarily classified into two categories, and their technological differences directly determine their application scenarios.


| Feature | Infrared | Laser |
| Light source | Infrared LED | Laser diode |
Principle | Utilizes the scattering/absorption of infrared light by particulate matter | Uses the scattering of laser light by particles to analyze light intensity and angle. |
Accuracy | Low, mostly used as a relative concentration reference | Highly accurate, measures PM2.5/PM10 mass concentration. |
Resolution | Low, difficult to distinguish between particles of different sizes | Highly accurate, distinguishes particle size. |
Airflow design | Usually fanless, relying on natural diffusion or passive air intake | Built-in fan for active air intake, stable airflow, and reliable data. |
Cost | Low | Higher |
Main applications | Low-cost consumer electronics, such as low-end digital displays (level display) in car air purifiers | Professional detectors, high-end air purifiers, fresh air systems, smart homes, air conditioners, and IoT monitoring stations. |
Conclusion: Infrared sensors are economical and suitable for qualitative or semi-quantitative scenarios that do not require absolute accuracy. Laser sensors, on the other hand, are the preferred solution for high-quality air quality management and intelligent linkage due to their precise data capture capabilities.