

 News
News Industry News
Industry News Electrochemical carbon monoxide(CO) sensors are fuel cell type sensors. Carbon monoxide gas and oxygen undergo redox reactions at the working electrode and counter electrode, releasing charges and forming an electric current. The magnitude of the generated current is proportional to the concentration of carbon monoxide and follows Faraday's law. The concentration of carbon monoxide can be determined by measuring the magnitude of the current.
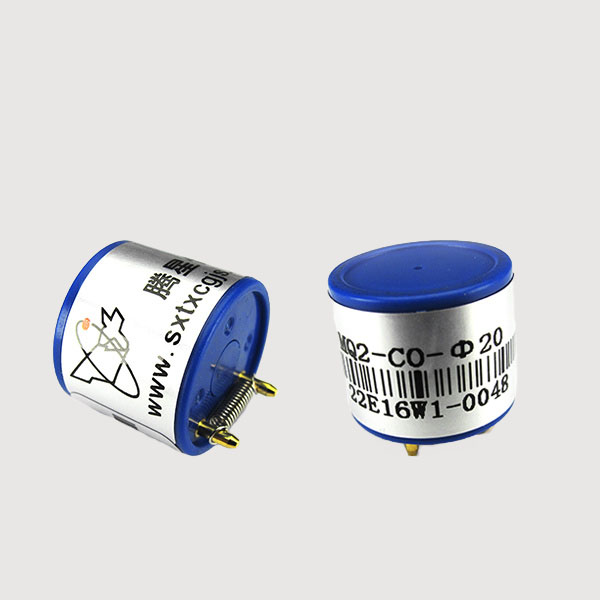

MQ-E2-CO Electrochemical CO Sensor
As a detection element, carbon monoxide sensors require careful maintenance during daily use. The following aspects should be noted when using the sensor:
Carbon monoxide usage precautions
1. Use the connector provided by the manufacturer during installation; do not directly solder the connector.
2. Aging time should be no less than 48 hours before use.
3. The sensor should not be subjected to excessive impact or vibration.
4. Avoid contact with organic solvents (including silicone rubber and other adhesives), paints, pharmaceuticals, fuel oils, and high-concentration gases.
5. Do not encapsulate the sensor with hot melt adhesive or sealant with a curing temperature higher than 80℃.
6. When the sensor is not in use, short-circuit the two electrodes to prevent electrode polarization.
7. Prolonged use in high-concentration gas environments exceeding the range may damage the sensor.
Frequently Asked Questions about Carbon Monoxide Sensors
Q1. Does a high sensor current directly affect its accuracy?
If the sensor's measurement current is high within its normal range, it will not affect its accuracy. However, if the sensor is measured beyond its range, causing excessive current, it will affect the sensor's accuracy and linearity. Severe over-range measurement can damage the sensor.
Q2. What causes low sensor data?
① Inappropriate gas source or gas path materials used during testing. Gas adsorption on the gas path materials leads to a lower actual concentration. It is recommended to use PTFE/PP/stainless steel materials for the gas path to reduce gas adsorption. Do not use silicone tubing, copper tubing, rubber, or other highly absorbent materials. (Especially for testing toxic gases such as NH3, H2S, and Cl2, the test gas path must be made of low-adsorption materials.) ② Replacing with other brands without calibration can result in a lower displayed concentration due to sensitivity differences.
Q3. What causes a slow sensor response?
A slow response will occur if the target gas concentration is too high.
Q4. What happens if the wrong voltage is applied to the sensor?
It will cause electrode polarization, which can severely damage the sensor. (Symptoms include a large zero-point deviation or an open circuit)
Q5 What will happen when the sensor reaches the end of its lifespan?
No signal, weak signal.
Q6 When measuring the sensor with a multimeter, the internal resistance is unstable and varies widely?
The sensor is essentially a capacitor; its resistance changes and cannot be measured with a multimeter.
If you have any needs of CO gas sensors, pls feel free to contact us~