

 News
News Industry News
Industry NewsIn a society where everything is connected, gas sensing technology has become the "invisible guardian" of development in various fields. In consumer scenarios, it protects home air quality; in the automotive field, it helps optimize exhaust gas and monitor safety; in industrial production, it ensures process stability and prevents disasters; in medical scenarios, it accurately detects respiratory gases to assist in diagnosis; in environmental monitoring, it captures pollutants in real time to protect the ecology. From daily life to macro production, gas sensing technology uses its keen "sense of smell" to promote various industries to move towards intelligence and safety. Here are some common gas sensing methods.
1. PID photoionization gas sensor
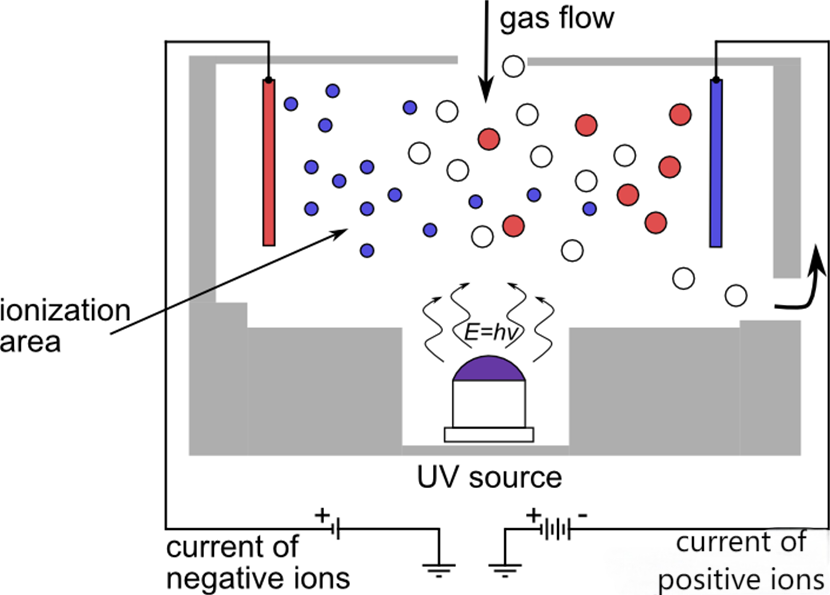
The core principle of PID (Photoionization Detector) is to use ultraviolet light (UV) to irradiate gas molecules to ionize them and generate detectable current signals. The typical structure of a PID sensor consists of an ultraviolet light source (UV lamp), an ionization chamber, an electrode system, a sampling system, and a signal processing circuit. PID is suitable for detecting volatile gases and vapors with ionization energy lower than ultraviolet light energy, mainly volatile organic compounds (VOCs), ammonia (NH₃), hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), hydrogen cyanide (HCN), phosphine (PH₃), etc. PID plays an important role in industrial safety, chemical leakage, gas station oil and gas volatility monitoring and emergency response, and gas detection at hazardous chemical accident sites.
2. Thermal conductivity gas sensors
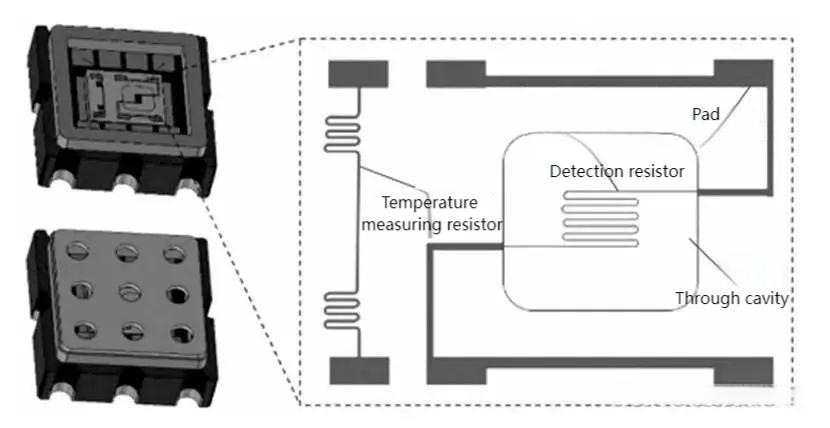
Use the difference in thermal conductivity of different gases. The sensor consists of a detection element (such as platinum wire) and a reference element to form a Wheatstone bridge. When the target gas enters the detection chamber, its thermal conductivity is different from that of air, causing the temperature of the detection element to change, the bridge to be unbalanced, and the output voltage signal proportional to the gas concentration. It can detect high concentrations of H₂, CO₂, or a component in a mixed gas (such as CH₄ in natural gas).
3. Non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) gas sensors
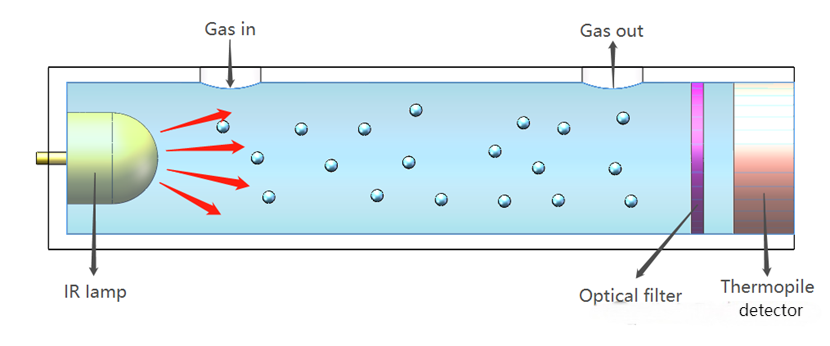
Are based on the selective absorption of specific infrared wavelengths by gases (such as the absorption peak of CO₂ at 4.26μm). The sensor consists of an infrared light source, a filter, a gas chamber, and a detector. The target gas absorbs infrared light of a specific wavelength, the light intensity received by the detector is weakened, and the gas concentration is calculated by the Lambert-Beer law. Greenhouse gases or toxic gases such as CO₂, CO, and CH₄ can be detected.
4. Laser gas sensors
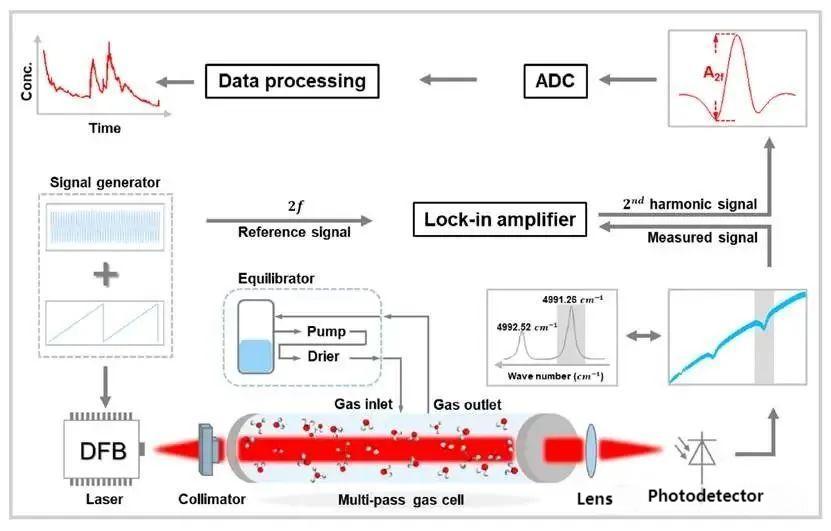
Laser gas sensors are divided into tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) and cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS). TDLAS is based on the Lambert-Beer law, uses a semiconductor laser to scan the characteristic absorption peak of the target gas (such as CH₄ at 1.65μm), and calculates the concentration by measuring the laser intensity attenuation. It has high resolution and anti-interference capabilities. The CRDS laser is reflected multiple times in a high-reflectivity optical cavity (reflectivity > 99.99%), and gas absorption causes the light intensity to decay exponentially. The gas concentration is determined by measuring the ring-down time (the time required for the light intensity to decay to 1/e of the initial value), and the sensitivity can reach the ppb level.
5. Catalytic combustion gas sensor
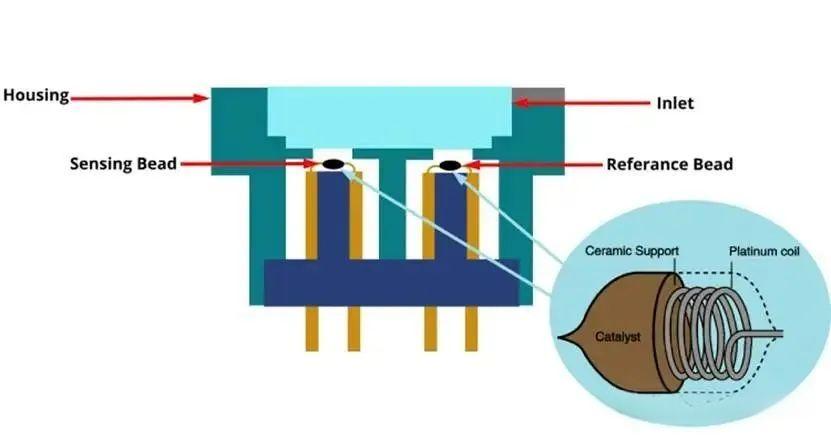
The combustible gas catalytically burns on the surface of the catalyst (such as platinum and palladium), releasing heat to increase the resistance value of the temperature sensor (such as platinum resistor). The gas concentration is detected by measuring the change in resistance. The sensor usually adopts a Wheatstone bridge structure, and the reference element is used for temperature compensation. Typical applications are the detection of combustible gases such as methane, propane, and hydrogen, and are widely used in industrial safety and gas leak monitoring.
6. Electrochemical gas sensor
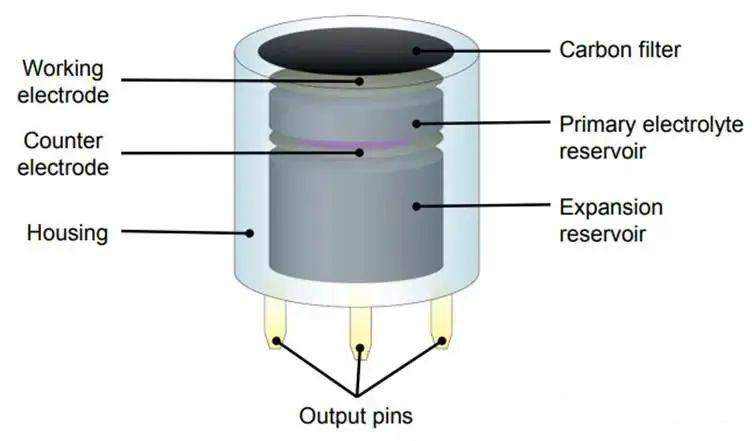
Commonly used electrochemical gas sensors are mainly constant potential electrolysis gas sensors and galvanic cell gas sensors. The principle of the constant potential electrolytic cell type is to drive the gas to react on the electrode by applying a constant voltage (such as CO oxidation at the working electrode), and the current generated is proportional to the gas concentration, which is suitable for detecting reducing gases (such as CO, H₂S). The principle of the galvanic cell type is that the gas undergoes a spontaneous redox reaction at the electrode, generating a current proportional to the concentration. For example, in an oxygen sensor, O₂ is reduced at the cathode and lead is oxidized at the anode, and the current directly reflects the O₂ concentration. Typical applications are the detection of oxidizing gases such as O₂, Cl₂, and SO₂.
For more information about gas sensors, please contact us:
ShanXi TengXing Sensor Technology Co.,Ltd
Website: www.tensensor.com
Email: [email protected]
Tel/WhatsAPP: 86 18335818384